Status Update: “Broken”.
Most athletes and a fair share of non-athletes have been there. The nature of our profession is that for the most part, we see people when they are down and out; our job is to diagnose the damage and to build them back not just to par, but to stronger than they were before the injury. My usual position as a Physiotherapist is to guide my patients from the tough day of diagnosis, through the often lengthy rehab process and safely back into their return to sport. We often get quite close to our patients and as athletes ourselves, ride the journey with them. In 2013 I was unlucky enough to flip the coin and be the one sitting in the sports physician’s office trying to swallow the gravity of my own injury situation: a stress fracture gone wrong following my latest Ironman triathlon. I think in this situation it’s arguably easier knowing less rather than more – I knew before the lovely Dr Chris Ball told me that I was looking down the barrel of major foot surgery, and a very long time away from my beloved sport.
Injury of any kind sucks, and I always advocate well-managed injury prevention program as “Plan A” but in reality, injuries happen – most athletes don’t have the most solid grasp on their self-preservation dial (and hey, I was beating my husband by 2 hours in that Ironman – there was no way I was pulling the pin so close to the end!). Jokes aside, there can be a silver lining. The team you have around you and your attitude are key to getting through the rough patch and flying out the other side as a more resilient and stronger athlete. As tough as injuries can be, I have learnt over the years from the process with countless patients as well as from my own experience post- foot surgery that there can indeed be a few upsides to injury:
- Learning opportunities:
- First and foremost, immediate questions need to be asked: What is the best course of treatment for short and long term outcomes? What are my options? (often there are a few good ones, especially where surgery vs conservative treatments are involved). How long will I have off my sport? Will this affect work/school etc?
- Once a course of treatment has been set that you as well as your health care team are happy with, the less urgent but just as important questions need to be asked: What went wrong? What will I do differently next time? Where is the weak link in the chain? How do we (as in, you and your Physio +/- surgeon and sports physician) build the body back to a point where it’s stronger than before? How can I prevent this from happening again? Do we need to change things upon return to sport (training load, technique, footwear etc)? Knowledge is power, and I cannot reiterate enough that you need to ask and ask until you get the answers that you need; your sanity during your rehab and your ability to avoid injury in the future depends on it. If you aren’t happy with your physio/doctor/surgeon, then find another one – you need to find the best quality care at all costs to get the best results.
- Respect for your body’s boundaries:
- So you found that mystical line in the sand, the actual safe limit of what your body can achieve; many never find it so you can take one thing away from the situation and that is that as an athlete, you are tough! But going forwards, if your injury was “overuse” in nature (ie stress fractures, tendinopathies etc) then you need to respect that boundary. Learn from it and take note of your body’s cues in future training and racing scenarios.
- If your injury was more traumatic in nature (eg broken tibia from a soccer clash or dislocated shoulder from a cycling accident), then there’s not a lot more you can do other than accept that playing sports involves risks. Given a choice, you’d still take those risks to sitting on the couch getting fat and unhealthy, right?!
- An Attitude of Gratitude:
- There’s nothing better than that moment your surgeon (or doctor or physio) gives you the go-ahead to do some exercise. Even if it’s technically “rehab” – “I’ll take it!” you yell as you hug them (Ok exaggeration. Only slightly though.) Prior to a major injury you may be guilty of complaining when the alarm clock goes off at stupid o’clock, if it’s cold/hot/raining; if the session is too hard…or not hard enough….If your race didn’t go perfectly, and so on. Afterwards I can honestly say that every single step I take is done with an “attitude of gratitude” – my coach and husband will vouch for the fact that every run is a bonus, every race is a bonus, and I am thankful to be able to have a fit, strong and healthy body again. Hell, I’m even grateful to be able to do the housework these days – taking an independent person and attaching them to crutches for 3 months is enough to send anyone crazy! I have been guilty of treating my body somewhat like a rental car in the past, but I now appreciate it and treat it much more lovingly (Karma, my friends, Karma…).
- Mental Toughness:
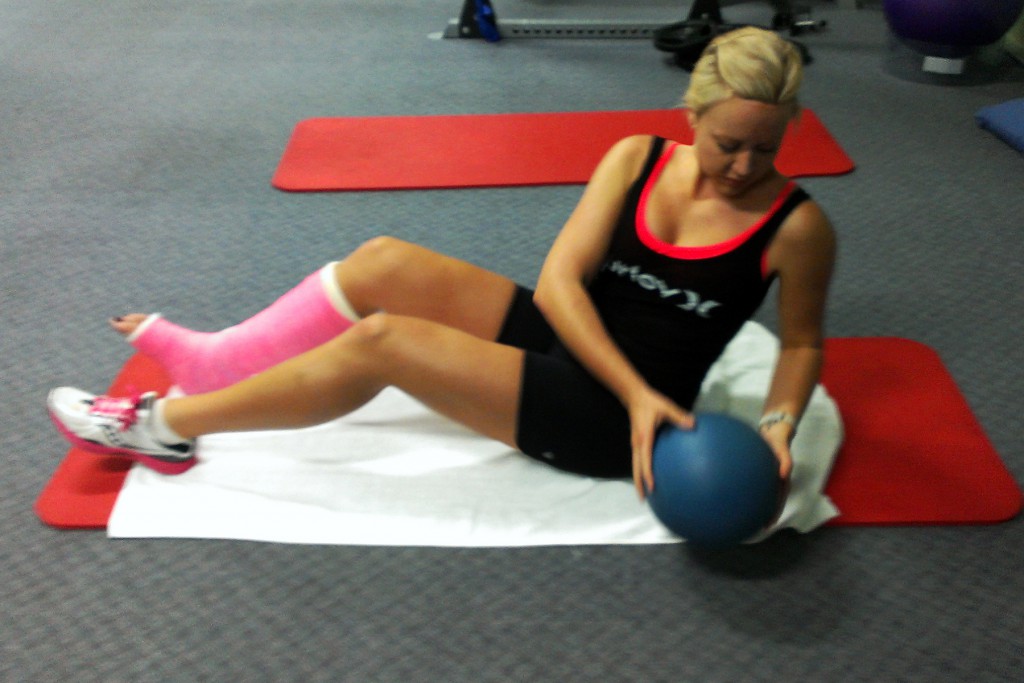
- And by this I don’t mean your ability to push through and “eat the pain” as my husband would say – if you got injured in the first place by pushing too far you definitely don’t need to learn this. But in my experience it’s often the athletes who are able to blindly push through that are also in need of some mental “balance”. I am by no means exempt from this generalisation. I took the time after my surgery to finally learn how to slow down and meditate (I highly recommend it, you’ll never look back), as well as to focus on other things in my life other than training 20 hours a week and working full time. It was not the most fun I’ve ever had – by choice I would much rather be working and training! – but it has taught me a sense of balance which I had never had in my life before, and I think that this has benefitted both aspects of my life well after the initial injury period. For most athletes I would therefore consider the slowing down process as “building mental toughness”, even if it’s not the traditional sense of the phrase.
- Absorption of training:
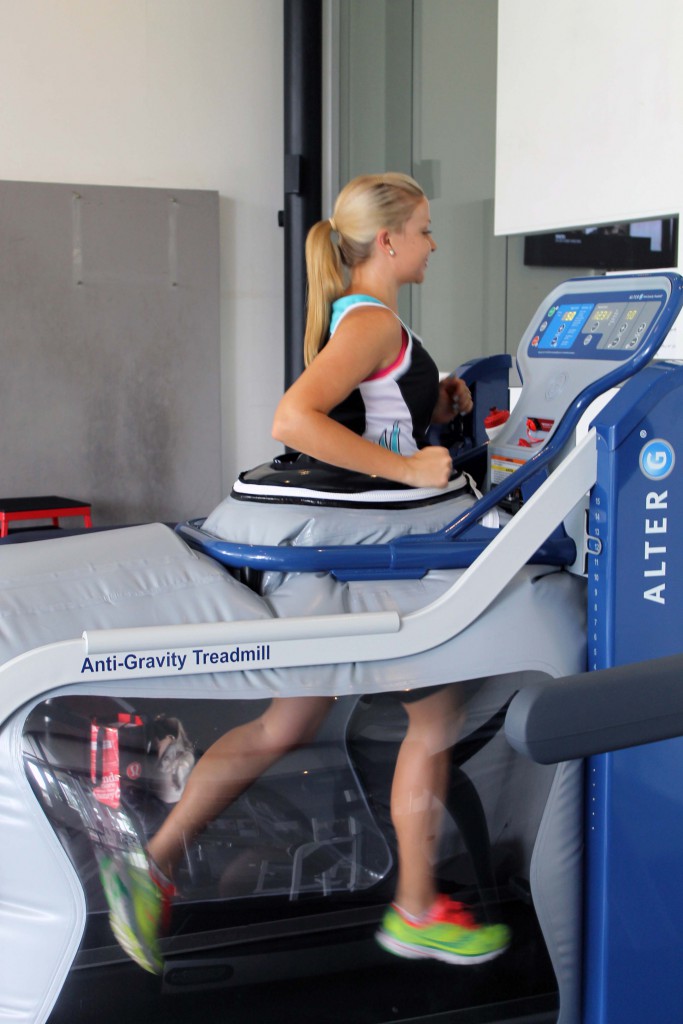
- A wise triathlete (Emma Snowsill) once said that if you don’t allow your body to rest, it will force you to via sickness or injury. I would put pregnancy in the same category here simply because the reduced training load while you’re growing a human has the same affect – time to let the body take stock. To absorb all the months/years of training it has done, and to build back a little stronger. As physios we educate patients on how a bone will actually be stronger where it broke after the healing has occurred, because extra bone is laid down in the healing process; this is a nice metaphor for the entire healing process of the body. Reassure yourself that you WILL come back from the injury, and that all the training you’ve done in the past will not be gone.
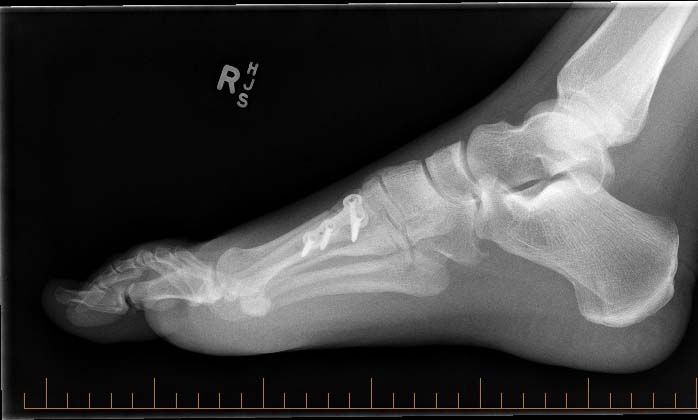
Sesamoid bone graft and 1st Metatarsal dorsiflexion osteotomy on my Right foot, done in 2013 by Dr Ben Forster
So there you have it, my version of what I’ve learnt through injury in a nutshell. I’ve kept many details of the injury and whole rehab process pretty close to my chest up to this point; as a physio it is not the easiest boat to be in. Physiotherapy may be my “day job” and I certainly love it, but I am first and foremost an “athlete” and in the past have certainly had trouble switching that part of my personality off, even if the Physio part of my brain is telling me something is a bad idea. As I get older and more experienced with both Physiotherapy and Ironman racing, I am learning how to strike the balance but it is always a work in progress. I am very fortunate to have two very patient and understanding men in my life in my husband Patrick Shannon and my coach Scott DeFilippis. Without them I would not be on track to be lining up again for Ironman NZ in 4 months’ time – 1 year post-baby and just over 2 years post foot surgery.
Hopefully this post will hit home with a few “broken” athletes out there and help to get you through and back to your passion. If you would like to follow my journey back to the Ironman start line you can find me on Instagram (@KRISTY_SHANNON), I’d love to have you along for the ride!
Kristy Shannon
B.Appl.Sc(HMS); B.PHTY(Hons)
Director and Principal Physiotherapist First In Physio